Difference Between MAC and IP Address
MAC Address
Difference Between MAC Address and IP Address: Each device connected to the network is given a 12-digit hexadecimal number called the MAC address, or Media Access Control Address. The Network Interface Card (NIC) often houses the MAC address, which is typically assigned during the manufacturing process as a unique identification. When trying to find a identifies the devices or run diagnostics on local network hardware, the MAC address identifies is necessary. An example of a MAC address is: 00:1B:44:11:3A: B7
The base and destination MAC addresses are included in the header of each data frame to facilitate clear node-to-node communication. MAC addresses are part of the data link layer of the Open System Interconnect (OSI) concept.
A device may have several MAC addresses since each device is given a distinct MAC address.
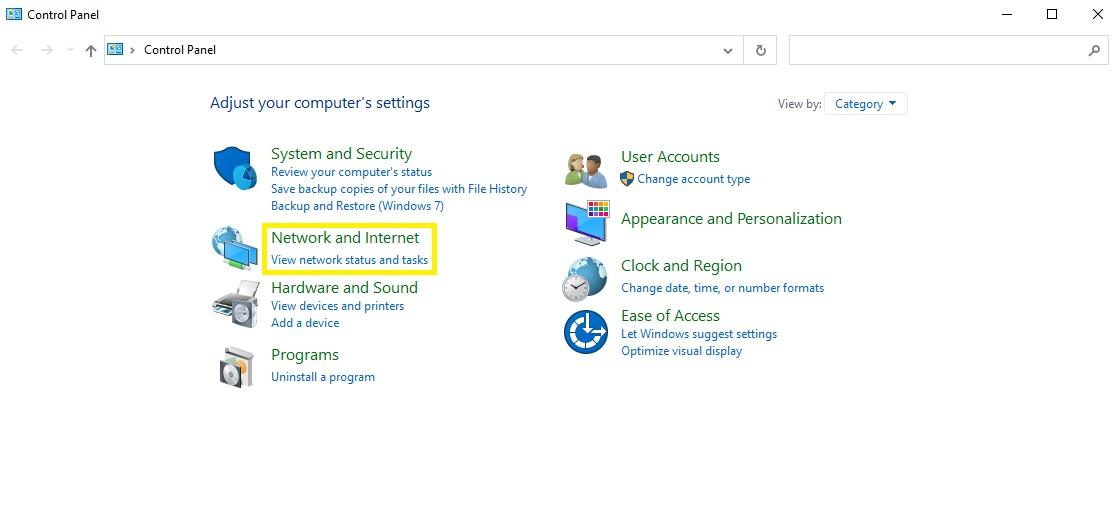
How to find MAC Address on Windows
- Select Network and Sharing Center by clicking Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet.
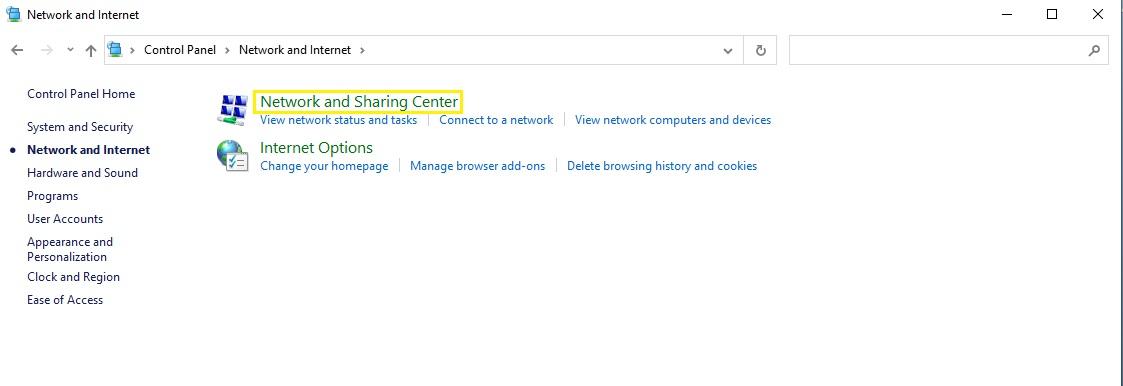
- Select the network whose MAC address you want to display by clicking it.
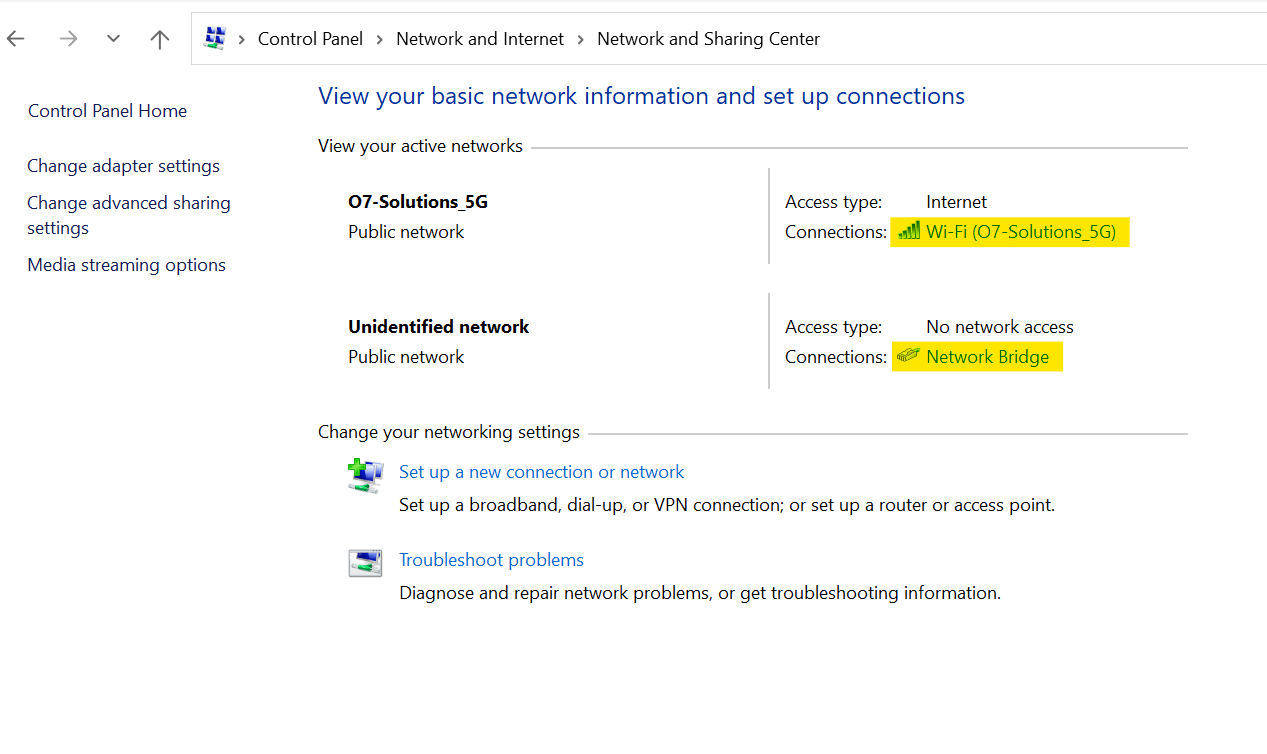
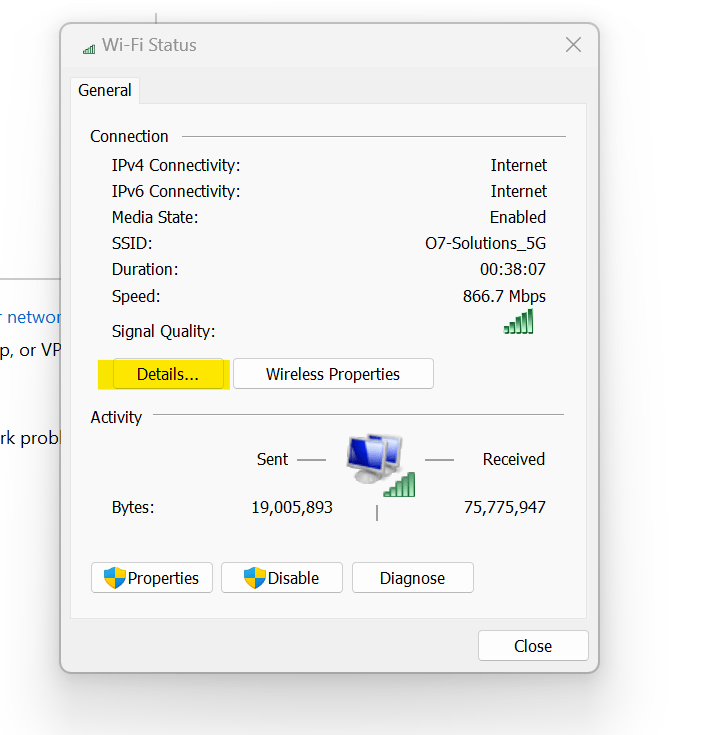
-
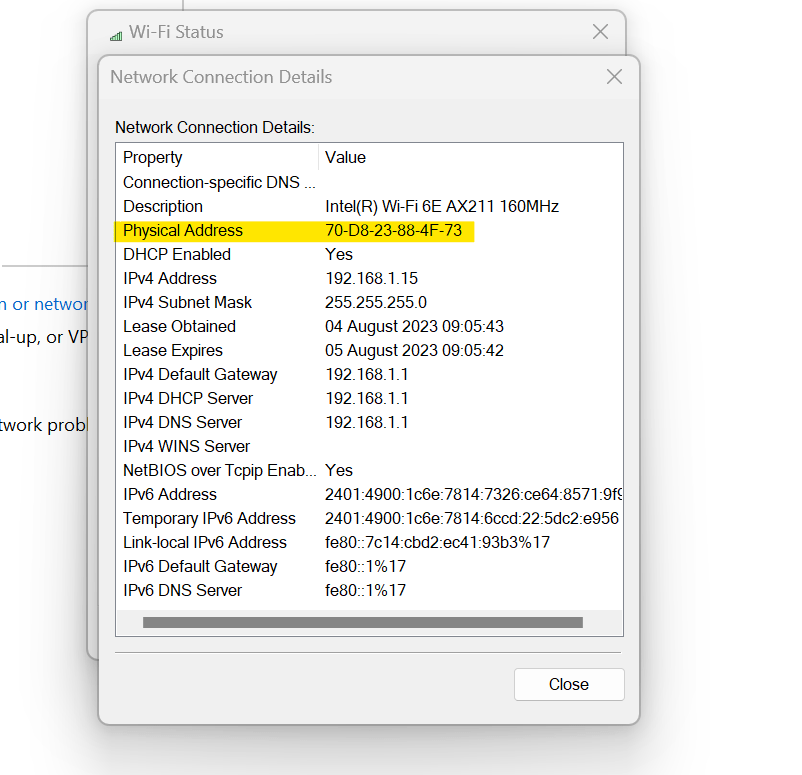
Under the header of “Physical Address,” the MAC address is displayed.
IP Address
IP address stands for Internet Protocol address and is a unique identifier for connecting to a particular computer or computer network which is provided by ISP (Internet Service Provider). An IP address allows a computer to send and receive data when connected to the Internet.
Two main versions of IP (Internet Protocol) IPv4 and IPv6 are used to create IP addresses. 192.168.0.1 is an example of an IPv4 address that is a 32-bit dotted decimal number, but an IPv6 address is a 128-bit hexadecimal number, for example 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370 :7334.
-
IPV4 –
There are four types of IP address:
- Private – This IP address is connected to every device you connect to the internet network, including laptops, desktop computers, smartphones, etc. Additionally, the demand for private IP addresses expanded significantly with the development of IoT (internet of things) technologies. The network device (router) must uniquely identify each system. The router would therefore be the sole device with the ability to create unique private IP addresses for each of them on the network.
- Public – The public IP address functions as the principal address for the entire network, containing all other network components connected to the network. The network assigns a private IP address to each device. The public IP address is assigned to the network equipment (router) under the supervision of the Internet service provider (ISP). ISPs gather a lot of IP addresses, which they then give to their customers.
It is possible to further classify public IP addresses into two subcategories:
Static – Unlike dynamic IP addresses, which are variable addresses, static IP addresses are, as their name suggests, constant addresses. The network device continuously assigns the system the IP address it was given. Companies and people steer clear of
- adopting static IP addresses because of their consistency. But if a business wishes to assign a host to its network server, they are necessary.
- Dynamic – These are the IP addresses that change frequently and are not consistent. According to the needs of the client, they are selected by the ISPs from a vast collection of IP addresses. In this manner, often changing IP addresses demonstrate cost effectiveness for ISPs and, to a certain extent, offer security against hackers and cybercriminals.
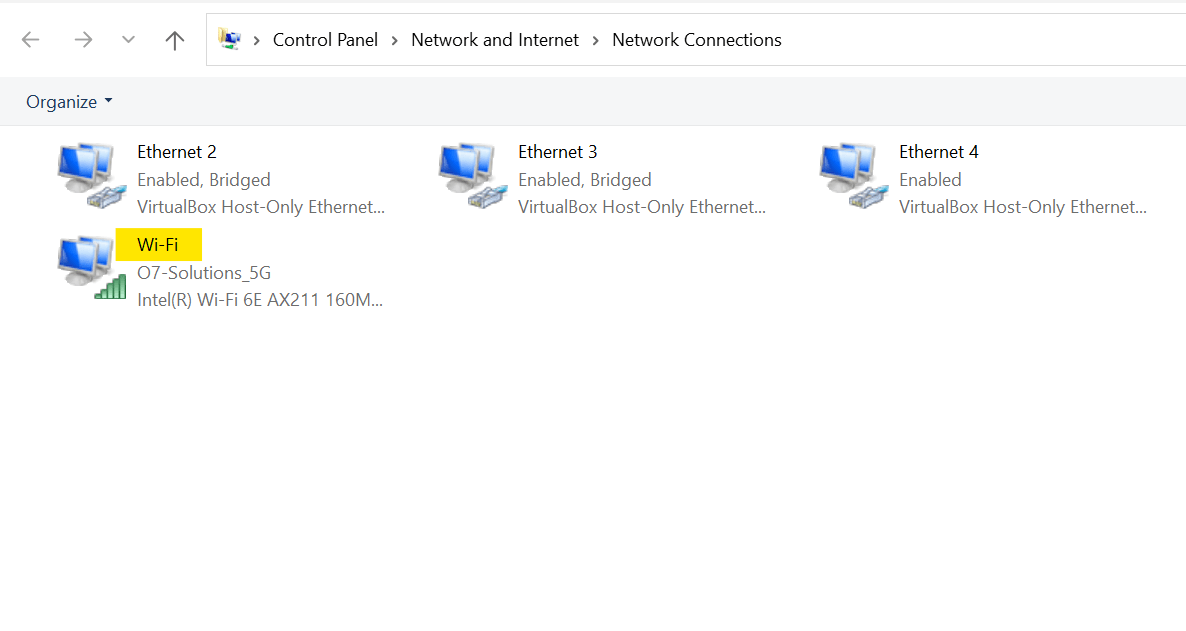
How to find IP Address on Windows:
- Press to the keyboard shortcut, Win +R to go to the Run Now type ncpa.cpl to view all the networks that you are connected with.
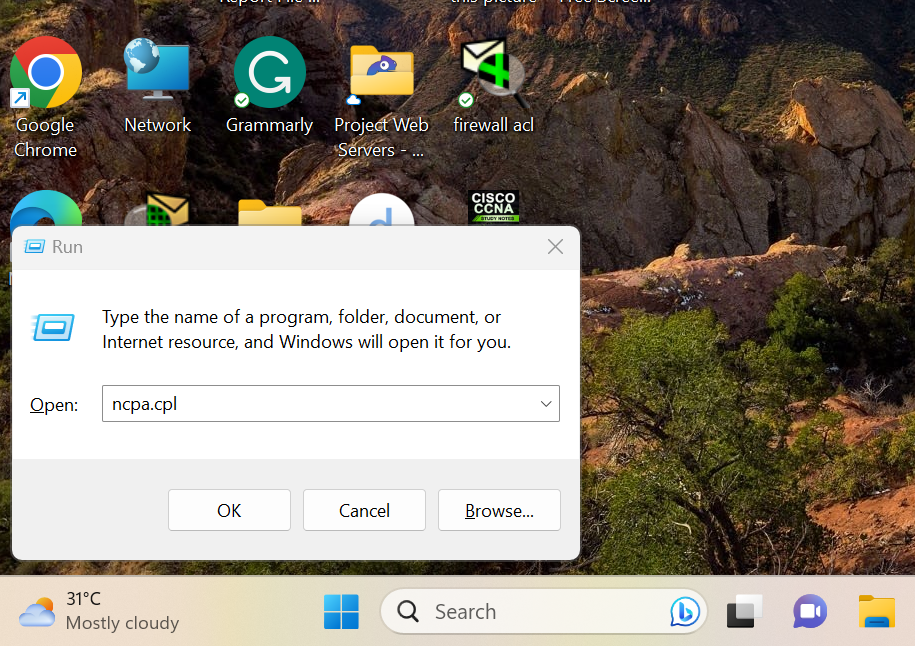
-
Select the network that you want to view the IP address of.
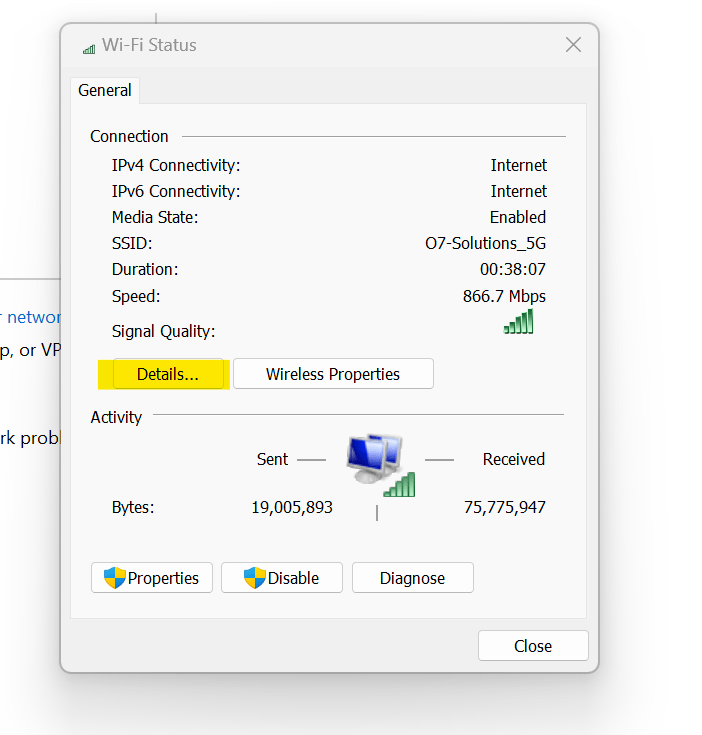
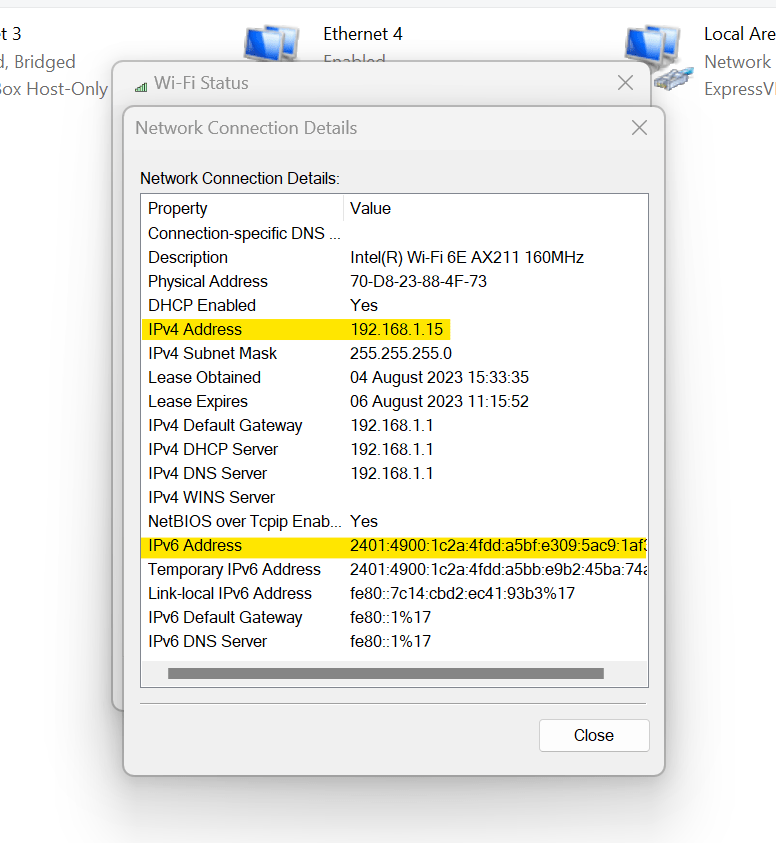
-
Here, both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are visible.












Leave a Reply